Active transport of MGMR offers the potential for intercellular delivery of diverse types biomolecules which does not damage plasma membrane integrity and reduces cytotoxicity.

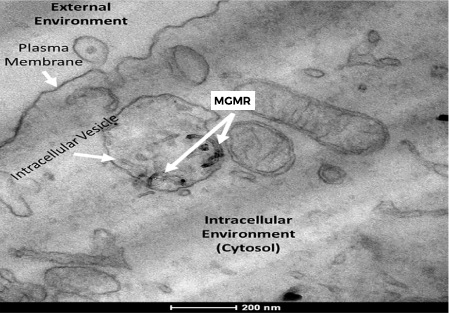
Mechanism of MGMR (CNT) Internalization:
- MGMR Vehicles dispersed in the extracellular space are encapsulated within intracellular vesicles,
- Vesicular trafficking into cellular interior,
- Vesicular plasma membrane breakdown and release of vehicles into cytosol.
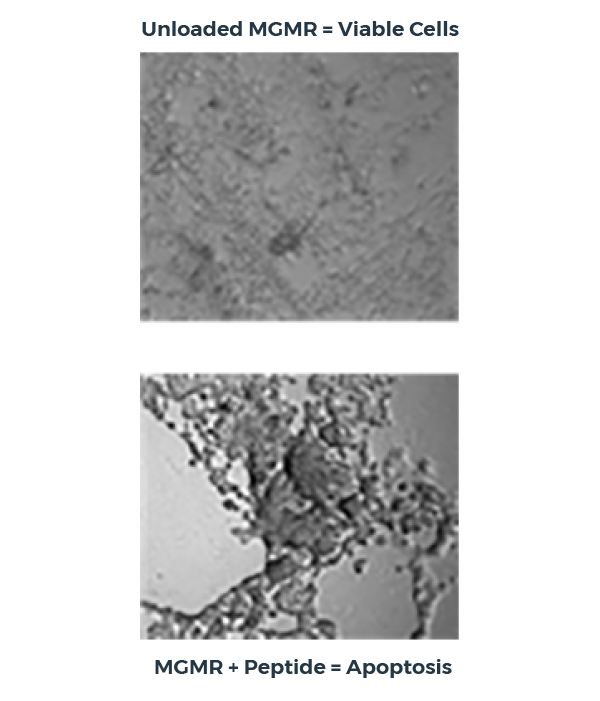
Intracellular peptide transport with MGMR
In this peptide delivery study, MGMR binds a pro-apoptotic peptide with high affinity, transports it across the plasma membrane, and releases it within the cytoplasm, triggering apoptosis. Critically, unloaded MGMR does not reduce cellular viability and the peptide alone demonstrates no significant effect.
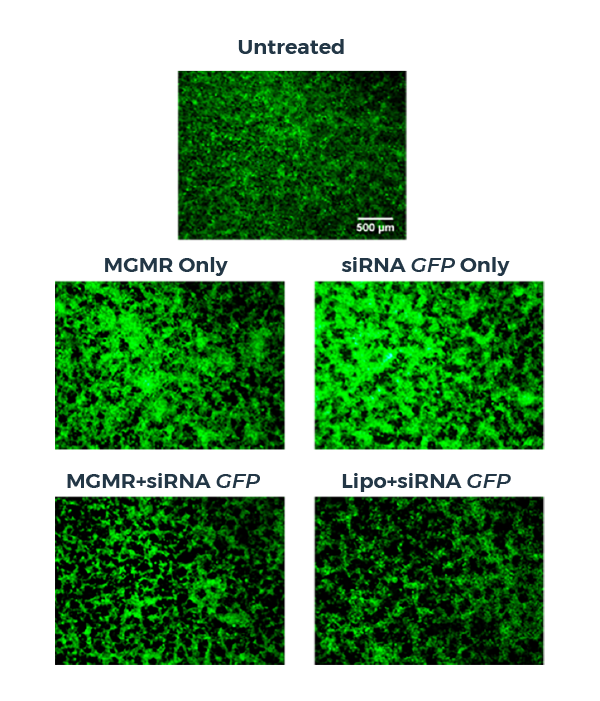
MGMR enables efficient intracellular transport of siRNA
In this siRNA delivery study, siRNA-loaded MGMR is readily internalized by cells, ferrying siRNA across the plasma membrane and delivering the payload into the cytosol. Efficiency of siRNA delivery is evaluated by mRNA-level expression of the gene of interest.